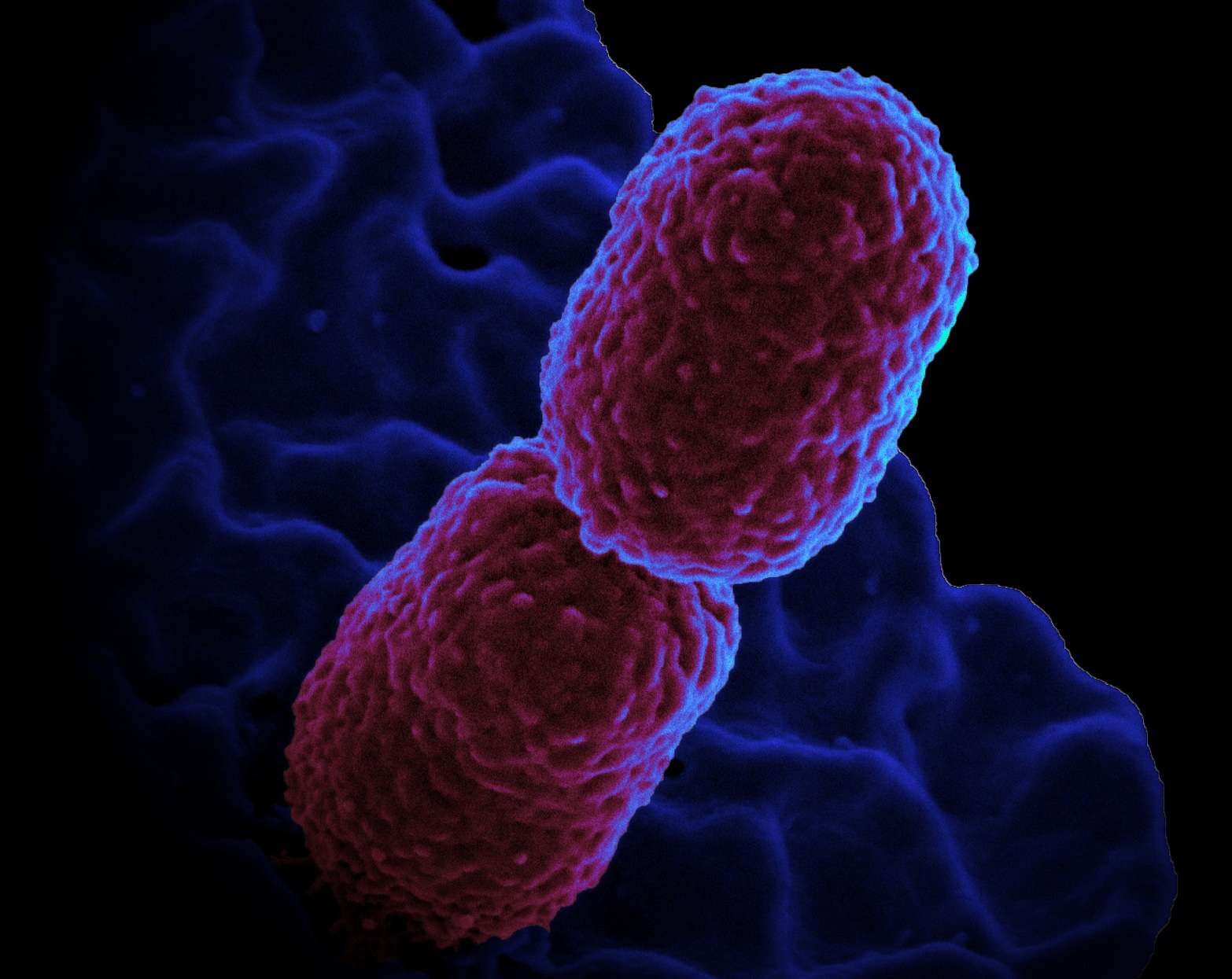
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a enterobacterium, i.e. a bacillus Gram negative. This bacterium immobile is commensal of the human intestine, but also of the upper airways.
A bacterium that causes infections (urinary tract infection, etc.)
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic bacteria that causesNosocomial infections (contracted in a hospital environment) such as cystitis, pneumonia and septicemia.
Klebsiella pneumoniae and its resistance to antibiotics
Klebsiella pneumoniae is naturally resistant to penicillins thanks to a uncomfortable chromosome. In addition, multiresistance has been observed among its strains. Some bacilli produce ESBL (beta-lactamases to spectrum extended), conferring resistance to beta-lactams.
In Europe, the frequency of bacteria Klesiella pneumoniae resistant to fluoroquinolones, to the cephalosporins third generation and aminoglycosides increased.
To treat infections involving multi-resistant bacteria, carbapenems may be used as a last resort. Cases of bacteria K. pneumoniae resistant to carbapenems have also been noted.
Interested in what you just read?
Subscribe to the newsletter The daily : our latest news of the day.
This will also interest you
Discover more future smart health innovation/ with AB SMART HEALTH







